Lose 2 mg Mazindol
€ 250,00
Lose 2 mg Mazindol
Lose 2 mg Mazindol is a dietary supplement used in conjunction with a low-calorie diet as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of exogenous obesity. Appetite squelcher and treatment for Obesity , Lose 2 mg is utilized in each of these applications. However, because it has the potential to become addictive, it is classified as a controlled substance in several countries.
Dosage Mazindol Lose 2 mg
Adults and adolescents should take 20–40 mg of this medication every 24 hours.
In most cases, it is advised that administration take place thirty to sixty minutes after each meal.
After 18:00 hours, the patient should no longer be given the finishing dose.
It is recommended that IFA Diety AP 20mg not be administered for more than eight weeks and that treatment should be stopped and started again based on clinical criteria.
Side outcomes IFA Diety AP 20mg
Anorexia, constipation, dry mouth, nausea, and transient spikes in liver enzyme levels might be expected to occur regularly.
Who should not take mazindol?
You cannot take mazindol if you
- have heart disease or high blood pressure;
- have arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries);
- have glaucoma;
- have taken a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), tranylcypromine (Parnate), or phenelzine (Nardil) in the last 14 days; or
- have a history of drug or alcohol abuse.
Mazindol Lose 2 mg
CNS and peripheral apprehensive system: inability to sleep, headaches, dizziness, tension, paresthesia, increased sweating, altered taste, and seizures; one patient with the schizoaffective disorder had likely been diagnosed with the condition before sibutramine developed acute psychosis after beginning treatment.
Cardiovascular machine: tachycardia, palpitations, elevated blood pressure (slight increase in blood strain at the relaxation of one three mm Hg and a moderate increase in heart rate with the aid of 3-7 beats/min), vasodilation (flooding with a feeling of warmth), exacerbation of hemorrhoids; in a few instances – a more significant pronounced increase in blood pressure and heart rate acceleration.
The urinary system might be affected by acute interstitial nephritis and mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis in sporadic cases.
Thrombocytopenia and Henoch-Schonlein purpura affect the blood’s ability to clot.
Although they become less severe and less common throughout treatment, most adverse effects manifest themselves early (within the first four weeks).
Be the first to review “Lose 2 mg Mazindol” Cancel reply
Related products
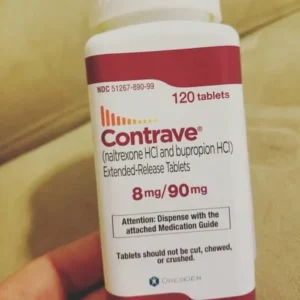
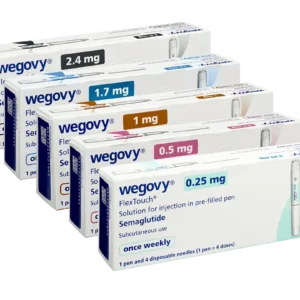
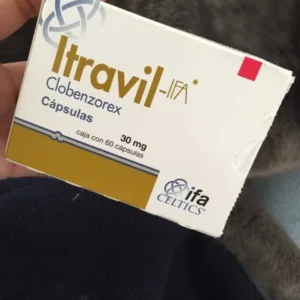
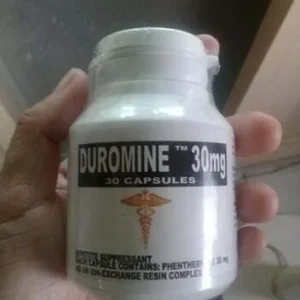
Diet pills




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.